Completion Plugin
The Completion Plugin provides intelligent, context-aware command-line autocompletion for your CLI applications. Built on top of Fig’s completion system, it automatically generates completion specifications that work seamlessly with Fig, Amazon Q, and other completion engines.
Features
- 🎯 Intelligent Autocompletion: Context-aware command and flag suggestions
- 🔧 Fig Integration: Native support for Fig’s completion system
- ☁️ Amazon Q Compatible: Works with Amazon Q development environments
- ⚡ Zero Configuration: Automatic generation of completion specs
- 🌍 Multi-language Support: Built-in internationalization support
- 🔄 Dynamic Updates: Real-time completion spec generation
- 📦 Plugin Architecture: Easy integration with existing CLI applications
Installation
npm install @hyperse/wizard-plugin-completionQuick Start
// @filename: @hyperse/wizard-plugin-completion/dist/index.d.ts
import { } from '@hyperse/wizard';
import { } from '@hyperse/wizard-plugin-completion';
const = ({
: 'my-cli',
: 'My CLI application',
: '1.0.0',
});
// Add completion plugin
.(());Basic Usage
Generate Completion Specs
The plugin automatically adds a completion command to your CLI:
# Generate completion specs and output the directory path
my-cli completion
# Or explicitly specify output flag
my-cli completion --output
Output Structure
When you run the completion command, it generates a .fig directory with your CLI’s completion specification:
/Users/username/project/.fig/
└── my-cli.jsThe generated file contains a complete Fig specification that includes:
- All available commands and subcommands
- Command descriptions and help text
- Available flags and options
- Flag types and validation rules
- Persistent flags (like
--help,--version)
Environment Setup
Amazon Q Configuration
For Amazon Q integration:
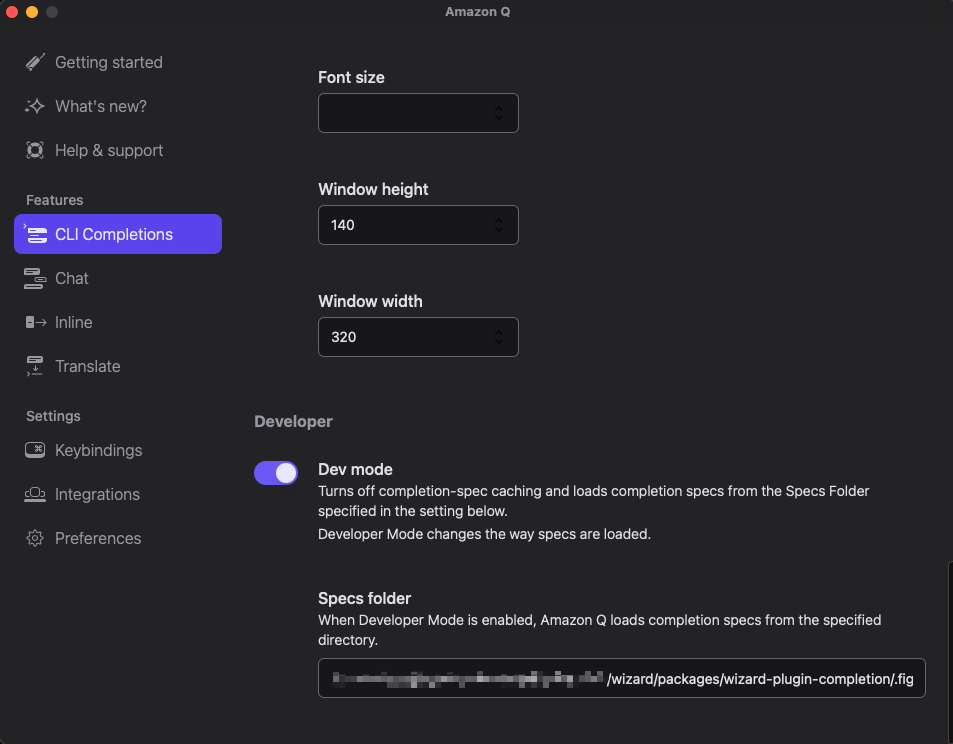
- Open Development Mode in Amazon Q
- Set Specs Folder to the directory containing your
.figfolder - Restart Amazon Q to load the new completion specs
Other Completion Engines
The generated Fig specs are compatible with other completion engines that support Fig’s specification format, including:
- Zsh completion
- Bash completion (with fig integration)
- Custom completion systems
API Reference
createCompletionPlugin()
Creates a new completion plugin instance.
Returns: Plugin - A wizard plugin that adds completion functionality
Example:
const completionPlugin = createCompletionPlugin();
cli.use(completionPlugin);Completion Command
The plugin automatically adds a completion command with the following options:
| Flag | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
--output | Boolean | true | Whether to generate the Fig spec and output its directory path |
Generated Spec Structure
The plugin generates a Fig specification that includes:
const myCli = {
name: 'my-cli',
description: 'My CLI application',
options: [
{
name: ['-h', '--help'],
description: 'Show help information',
isPersistent: true,
},
{
name: ['-v', '--version'],
description: 'Show version information',
isPersistent: true,
},
],
subcommands: [
{
name: 'build',
description: 'Build the project',
options: [
{
name: ['--target'],
description: 'Build target',
},
{
name: ['--watch'],
description: 'Watch for changes',
},
],
},
],
};
export default myCli;Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Q: Completion not working in my terminal A: Ensure Fig is properly installed and the generated specs are in the correct location. Try restarting your terminal or Fig.
Q: Generated specs are not updating A: Run the completion command again to regenerate the specs. The plugin creates fresh specs each time.
Q: Amazon Q not recognizing the specs A: Make sure you’ve set the correct specs folder path in Amazon Q’s development mode settings.
Q: Some commands not appearing in completion A: Ensure all your commands are properly registered with the wizard before adding the completion plugin.